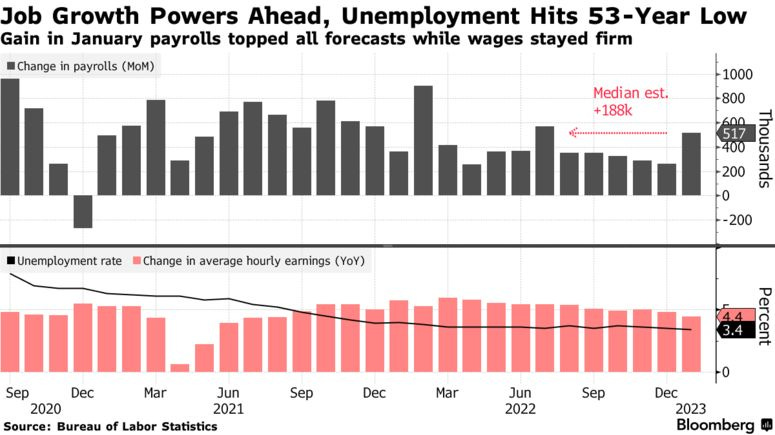
The effect of Jobs Posting in US
In previous weeks, we had heard about the U.S. payrolls added 517,000 jobs, which is usually a great deal for the economy. Ironically, this sent a strong signal to the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates aggressively.
Source: Bloomberg
In fact, on Wednesday February 08, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell had delivered some key messages that were believed to point at interest rates needed to keep rising to quash inflation.
“We think we are going to need to do further rate increases,”
“The labor market is extraordinarily strong.”
If the job situation remains very hot, “it may well be the case that we have to do more,” he said.
His comments tend to the meaning of pressure in the labor is an important factor requiring easing in order to cooling off inflation in core services, excluding housing.
Fed Bank of New York President John Williams also adjusted to the issue
“That still seems a very reasonable view of what we’ll need to do this year in order to get supply and demand in balance and bring inflation down,”
Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari, an FOMC voter this year, who told the Boston Economic Club that rates will need to rise higher to combat the wage growth.
“There’s not yet much evidence, in my judgment, that the rate hikes that we’ve done so far are having much effect on the labor market,” he said. “We need to bring the labor market into balance so that tells me we need to do more.”
It is seem like most of the comments from Fed officials are to caution investors not to be complacent about the soaring S&P 500 and other indexes, as inflation remains a threat and the battle against it is not over. They have indicated their intention to stick to the median projection (in December) of 5.1% for rates this year.”
Source: Bloomberg
MORE REFFERENCES ABOUT FED’s PRESIDENTS ARE LIKELY TO PREFER HIKING AFTER JOBS POSTING
Fed’s Bostic Says Higher Peak Rate on Table After Jobs Blowout
Fed’s Kashkari Says Strong Jobs Data Show Need for More Hikes
Fed’s Williams Says Peak Rate Forecasts Still ‘Very Reasonable’
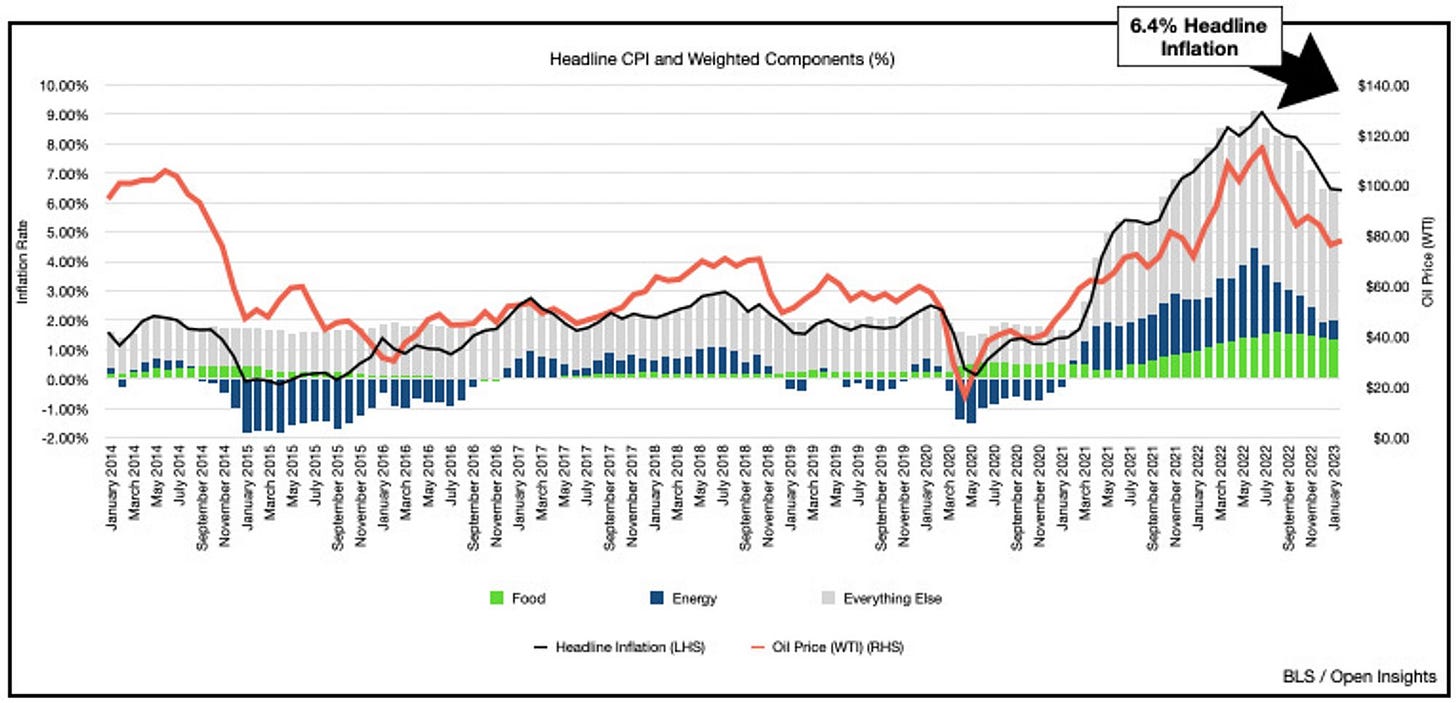
Inflation is slightly decrease but what is the main point?
On Tuesday, February 14, CPI of United State was announced with 10 bps decrease from the previous of 6.5%, which is higher that 6.2% expectation.
Source: Open Insights
But that was not the only disappointment when the core CPI moved up 10 bps to 0.4%, correct with the forecast, let deep into this problem a bit!
Source: Open Insight
Energy prices are the only ones that have been significantly affected by the interest rate and government policies. Other sectors such as Housing, Food and Services remain high and could rise further if employment improves. In the next few months, official economic data may show a temporary decline in inflation, but this could reverse and accelerate later. This would be detrimental for risk assets. The current economic indicators may look positive, but the future is uncertain. If inflation does not slow down more quickly, we may face serious consequences.
Moreover, this persistent inflation could have 3 potential impacts on the future economy, as it is a key factor for the government to monitor and adjust policy.
Those effected paths are a Soft Landing, Hard Landing and Non-hard Landing
Source: kyla’s Newsletter
The economy is still doing well. The labor market is robust. Retail sales surged in January. People are eager to spend money. The concern now is that inflation has reached a new normal level of 4-5%.
One more thing: The US potential Debt-Ceiling Crisis
In the United States, the debt ceiling is a limit on how much national debt that Congress lets the Treasury Department incur. And, unfortunately, the U.S. government is the most indebted it has ever been. Its spending is out of control!!!
Congress has increased the debt ceiling 78 times since 1960 and currently, the debt of United State is $31 Trillion. And with the interest rate keeps moving on, they might not be able to pay for their debt.
Interest payments on federal debt have soared to nearly $900 billion per quarter in 2022, up from about $100 billion in 2020. This alarming trend shows no signs of stopping or slowing down, as the U.S. government continues to borrow more money to finance its spending.
However, borrowing is not the only option for funding public services and programs. The government could also reduce its spending or increase its revenue by printing more money or raising taxes. These alternatives have different implications for the economy and society, and they are at the center of two major debates currently taking place in the country.
According to Bonner Private Research,
The solution, from the government’s perspective, is currency debasement. Effectively, what debasement does is push losses onto the currency market and off nominal prices in the bond and stock markets. It socializes losses. It turns the dollar into a release valve. It puts a bid under nominal stock, bond and real estate prices.
And that’s what we’ve been calling inflation volatility or “inflate or die”. It’s the vacillation between deflation and currency debasement by the Feds, as they try to keep the government solvent during the collapse of the greatest ever debt bubble.
This is why it’s so important to watch the stock market in terms of gold (or purchasing power) from now on. You have to factor in the currency debasement into stock returns. It’s the only way to see the true performance of your investments.
Personal Information:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/kienquoc03/
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/quoc-nguyen-1131aa19a/
If you find it interesting, useful and want to receive more readings, please subscribe to your email below! Thanks for your interest